Introduction
Gliomas are common intracranial malignancies. Tumors show invasive growth, unclear boundaries and easy to recur. They are the most common primary tumors in the brain. Surgical treatment of brain functional gliomas is a neurosurgical clinic. A difficult job.
Patient Information
Gender and age:Thirty-two patients with glioma located in different parts of the cerebral hemisphere underwent neuronavigation surgery, including 18 males and 14 females; aged 33 to 72 years, mean age 58 years.
Lesion site:Located in the frontal lobe in 15 cases, located in the temporal lobe in 2 cases, located in the frontotemporal junction at 12 sites, located at the frontal and apical junction in 2 cases.
Nature of the lesion:There were 14 cases of astrocytoma, 13 cases of anaplastic astrocytoma, 2 cases of oligodendrocyte, 1 case of oligodendroglioma and 2 cases of glioblastoma.
Heal Force Excelim-04
【1】Planning before operation
Prepare the skin one afternoon before the operation and paste 6 to 8 markers on the scalp of the patient. Attach the marker to the difficult-to-move area and cover the lesion as much as possible. Cranial MRI scanning, imaging parameters: layer thickness of 2 ~ 4mm, layer spacing is 0, the matrix is 256 × 256, axial scan. The imaging information was imported and the computer reconstructed the three-dimensional image to calibrate the lesion.
【2】Patient Registration
The patient was then instructed to navigate the operating room. After successful anesthesia, the head was fixed with a mayfield head. Start the navigation station, install the reference ball rack, adjust the arm of the infrared camera, and complete the registration with the navigation probe.
【3】Approach Development
According to the anatomical location of the lesion and its adjacent structural relationship, the surgeon can choose the best surgical approach, including skin incisions, bone flap size, and lesion distance.
Navigation during operation:The surgeon can use a navigation bar or a registered surgical instrument to determine the position of the cortex incision, look for lesions, avoid important adjacent anatomical structures, and observe the extent and extent of the resection.
【4】Documents, data storage and processing
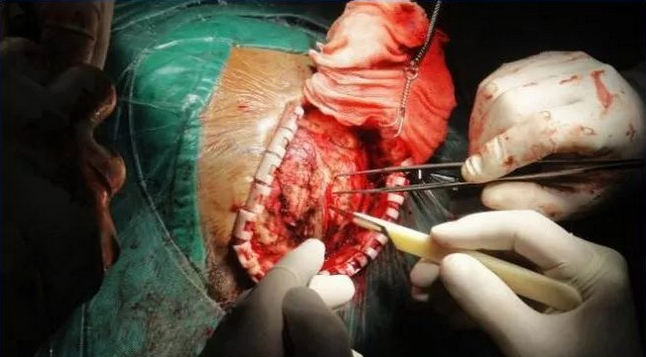
Brain glioma craniotomy
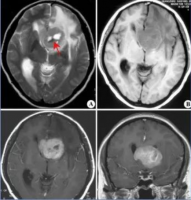
Glioma CT and MRI fusion pictures
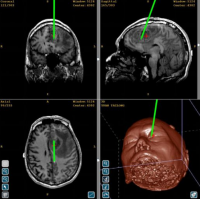
Clinical patient glioma Heal Force Excelim-04 system image
Operation result
Navigation surgery was successful in all 32 patients selected. The navigation accuracy of this group of cases was (1.2±0.5)mm. The average preoperative preparation time was 30 minutes, and the average operation time (including registration time) was 15 minutes. Within 72 hours after the operation, head M R I was scanned and enhanced. Imaging data showed that there were no signs of residual tumors in 30 patients (85.7%).
Neurological examination:All patients were generally improved after surgery, without serious complications such as infection. Of the 3 patients with lesions adjacent to the motor area, 1 had no effect on postoperative muscle strength, 2 had a postoperative decline, and had basically recovered to preoperative levels on discharge; 5 patients had speech function in the vicinity of the language center. It was not significantly affected; 3 cases of lesions adjacent to the thalamus basal ganglia received preoperative postoperative muscle strength, and 1 patient had short-term hyperthermia after operation. Body temperature returned to normal 4 days later. During 2 to 24 months of short-term follow-up, 2 patients (all glioblastomas) relapsed after 9 to 11 months of postoperative recurrence.
After-operation Review
The role of Heal Force excelim-04 surgical navigation:
1) Using imaging data before surgery to calibrate the tumor boundary in advance to minimize the design of scalp incision and craniotomy and reduce surgical trauma;
2) According to the calibration of the tumor boundary, the tumor volume was estimated preoperatively to facilitate the medium volume resection of the lesion.
3) Intraoperative warning to avoid damage to important blood vessels and nerves around the lesion;
4) Intraoperative reconstruction of dynamic trace lesions using three-dimensional images to observe the extent of tumor resection at any time and improve the ability of neurosurgeons to excise gliomas to the maximum;
5) Neuronavigation surgery for excision of glioma patients can reduce medical costs and reduce the likelihood of postoperative review.
Heal Force Excelim-04 surgical navigation application notes:
The most critical factor in the application of neuronavigation in glioma surgery is the accuracy of its navigation. It includes the accuracy of registration, the accuracy of digital systems, and the influence of brain displacement caused by various reasons on the lesions. During surgery, the craniotomy is one of the most significant factors affecting navigation accuracy. Preoperative dehydration of mannitol, release of cerebrospinal fluid during surgery, and resection of diseased tissue can cause brain tissue shift due to gravity.
Heal Force Excelim-04 Surgical Navigation Assisted Clinical Practice for Reducing Brain Drift Imaging:
1) Do not dehydrate mannitol as much as possible during surgery;
2) During intraoperative navigation, brain tissue can be used to gently "reset" the displaced brain tissue and reduce brain displacement.
3) Avoid early opening of the ventricle or brain pool during surgery;
4) For tumors in adjacent functional areas, intraoperative boundaries can be separated under navigation guidance, and then the tumor tissue can be removed again.
Heal Force Excelim-04 Neurosurgical Navigation System
Rich fusion
Compatible with DTI/PET/DSA/CTA/PCA/MRA/MRV/
T1 MRI/fMRI/Bold MRI/MRS Image fusion and processing
﹀
Clear reconstruction
Reconstructed 2D images and 3D models with clear details
Supports Fusion Modeling of Multiple Medical Image Sequences
﹀
Easy Planning
Can simulate multiple surgical approaches
Tomographic image length measurement
Automatic measurement of lesions
﹀
Accurate Navigation
Positioning error is less than 1mm
Multiple ways to correct brain drift
 沪公网安备31011802003750号
沪公网安备31011802003750号